The intended function of blockchain technology was never to operate in isolation from the larger economic ecosystem. Despite the challenges that cryptocurrencies pose to conventional financial practices, the practical applications of blockchain would be severely curtailed if it could not engage with external sources. However, the question of how to import off-chain data without compromising blockchain’s fundamental decentralization remains a pressing challenge
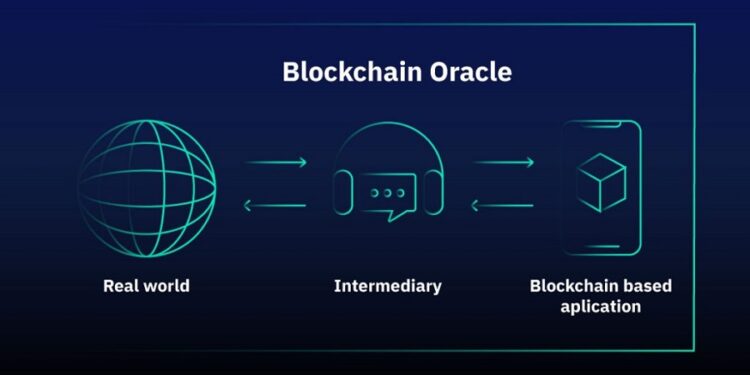
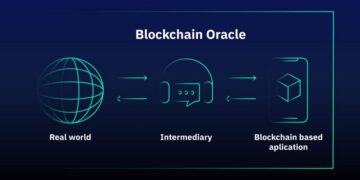
Blockchain oracles are advanced services that provide a solution to the complex task of importing trustworthy off-chain data into Web3. These decentralized blockchain oracles are crucial for the current advancements in decentralized finance (DeFi) as high-quality data feeds are essential for the success of DeFi applications. In the context of blockchain technology, an oracle acts as a bridge between the on-chain and off-chain worlds by providing reliable information from outside sources that can be used in smart contracts. This enables the realization of innovative and sophisticated smart contract applications that require trustworthy external data. Hence, it is important to understand the role of an oracle in the blockchain ecosystem and how it functions in the world of cryptocurrency.
Table of Contents
ToggleSolving the Oracle Problem
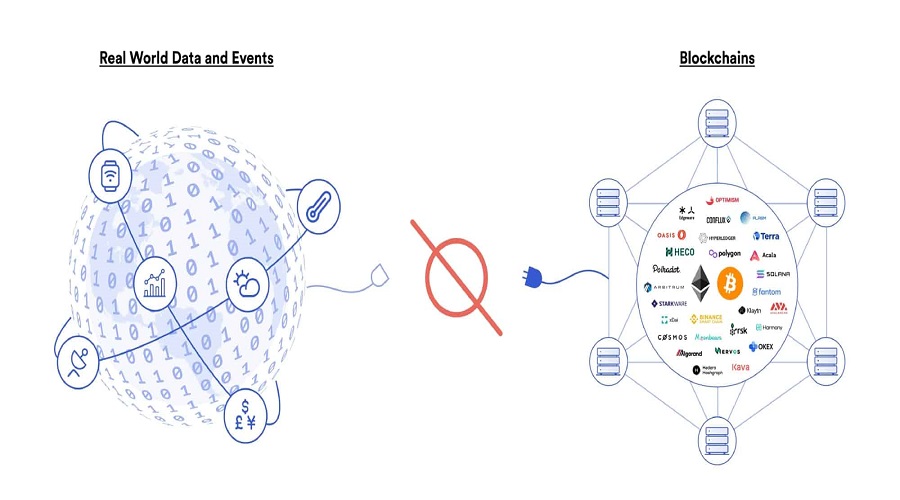
The blockchain oracle problem exposes a fundamental limitation of smart contracts, which is their inability to inherently interconnect with data and systems existing outside their native blockchain environment. External resources are referred to as off-chain, whereas data already stored on the blockchain is considered on-chain. By virtue of being intentionally isolated from external systems, blockchains gain their most valuable properties, such as strong consensus on the validity of user transactions, prevention of double-spending attacks, and network downtime mitigation. An additional piece of infrastructure known as an “oracle” is required to securely interoperate with off-chain systems from a blockchain, bridging the two environments.
The resolution of the oracle dilemma bears immense significance as the majority of smart contract use cases, particularly Decentralized Finance (DeFi), necessitate knowledge of real-world events and data that occur off-chain. Consequently, oracles widen the range of digital agreements that blockchains can facilitate, by providing a universal gateway to off-chain resources while preserving the valuable security attributes of blockchains. Various significant industries reap considerable benefits from combining oracles and smart contracts, such as finance’s asset prices, insurance’s weather information, gaming’s randomness, supply chain’s IoT sensors, government’s ID verification and an array of other sectors.
The accuracy of the oracle mechanism is of paramount importance in ensuring the successful execution of smart contracts, as the data provided by oracles plays a decisive role in determining their outcomes within blockchains. Therefore, meticulous attention must be paid to the design and implementation of the oracle mechanism to guarantee an error-free operation of the agreement.
What are blockchain oracles?
Blockchain oracles are instrumental entities that enable the seamless integration of blockchain technology with external systems, thereby enabling the smooth execution of smart contracts based on real-world inputs and outputs. This innovation has provided the Web 3.0 ecosystem with a formidable method of establishing a connection to existent legacy systems, data sources and sophisticated computations.
The utilization of decentralized oracle networks (DONs) facilitates the execution of hybrid smart contracts, where off-chain infrastructure and on-chain code are harmonized to create intricate decentralized applications (DApps) capable of responding to real-world happenings and engaging with established systems.

Suppose that Alice and Bob have expressed their mutual desire to place a financial wager on the conclusion of a horse race. In accordance with their agreement, the total amount of $80 has been transferred to the governance of a smart contract, wherein Alice has bet $50 on the triumph of team X and Bob has wagered $30 on the glory of team Y. The query remains as to how the smart contract is to determine the rightful recipient of the funds once the event is concluded. The resolution to this predicament is the implementation of an oracle mechanism, which entails the procurement of precise and authentic match results from an external source and their secure and dependable transference onto the blockchain platform.
The deterministic architecture of the blockchain mandates that every node on the network must derive identical results for a given input owing to its distributed ledger mechanism. Consequently, in the event of a node attempting to authenticate a transaction made by another node, it would encounter a different result, thereby upholding the system’s deterministic architecture.
Consensus, a well-established technique in blockchain technology, is utilized to facilitate agreement on a data value among nodes in the network. For nodes to reach consensus, determinism is a crucial requirement. This is demonstrated through well-known methods such as proof-of-work (PoW) with Nakamoto consensus and proof-of-stake (PoS) with Byzantine consensus, which may be familiar to some. The fundamental factor that enables the functionality of the blockchain is the ability to establish consensus.
The blockchain industry is facing the challenge of bridging the gap between the virtual and physical world. In order to fully utilize the potential of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), it is critical to integrate the pricing of Ether and other cryptocurrencies into contractual agreements. Additionally, reliable meteorological data is essential for the development of decentralized, trustless insurance systems. Moreover, data is crucial for the successful implementation of smart contracts, one of the fundamental uses of blockchain technology. Thus, considering the current limitation, the question arises on how can we effectively connect these two worlds.
The purpose of this guide is to provide an explanation of the functions served by blockchain oracles, elucidate the challenges faced in utilizing them (known as the blockchain oracle problem), and introduce a range of blockchain oracle projects currently underway.
Types of Blockchain Oracles
The broad assortment of off-chain resources has resulted in the proliferation of different types of blockchain oracles. Hybrid smart contracts demand the incorporation of diverse varieties of external data and computing power, as well as various modes of delivery and levels of security. In general, each form of oracle necessitates a blend of fetching, validating, computing upon, and distributing data to a particular endpoint.
Input Oracles
Currently, the prevailing category of oracle is referred to as an “input oracle” that obtains information from off-chain sources in reality and transmits it onto a blockchain network for the usage of smart contracts. These particular oracles are employed in fueling Chainlink Price Feeds, facilitating on-chain accessibility of financial market data for DeFi smart contracts.
Output Oracles
“Output oracles” are a contrasting counterpart to input oracles; these oracles enable smart contracts to transmit directives to external systems in order to initiate specific operations. Such operations encompass prompting a banking network to initiate a payment, requesting a storage provider to preserve received data, or signalling an IoT system to unlock a vehicle door upon successful completion of the on-chain rental payment.
Cross-Chain Oracles
Cross-chain oracles can facilitate the exchange of information and assets between different blockchains. These oracles are capable of reading and writing information across blockchains, which enables interoperability and the seamless transfer of data and assets. Cross-chain oracles play a crucial role in allowing data from one blockchain to trigger a reaction on another and in linking assets across different chains so that they can be utilized outside of their native blockchain.
Compute-Enabled Oracles
“Compute-enabled oracles” are a recent addition to the smart contract technology, which have gained popularity due to their ability to offer decentralized services that cannot be provided on-chain because of various restrictions such as technical, legal or financial constraints. The application of such oracles includes triggering smart contracts events using “Chainlink Automation,” computing “zero-knowledge proofs” to ensure data privacy and running a “verifiable randomness function” to provide tamper-proof and provable randomness to smart contracts.
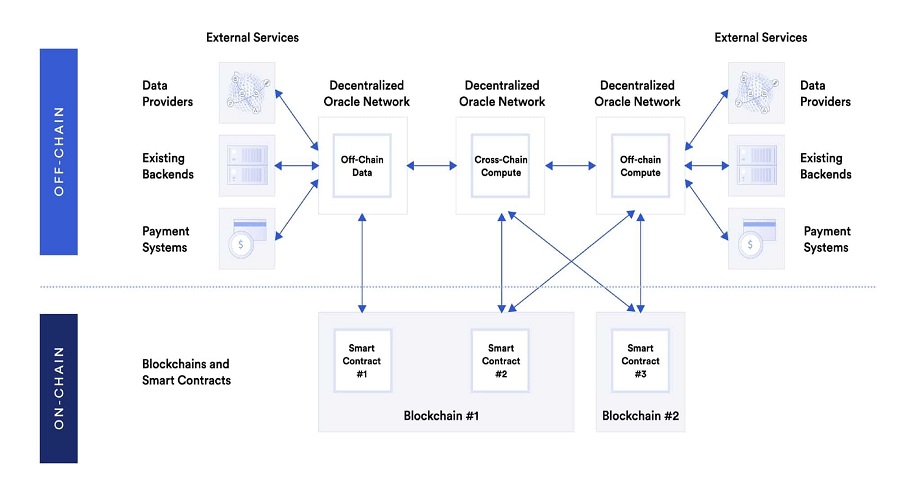
Blockchain Oracle Use Cases
Oracles are utilized by smart contract developers for constructing highly sophisticated decentralized applications that cater to a diverse range of blockchain use cases. Although the possibilities are virtually limitless, the following are the primary use cases that have gained widespread acceptance.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
When it comes to the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, a considerable portion of it relies on oracles for obtaining financial data pertaining to assets and markets. For instance, price oracles are utilized by decentralized money markets for the purpose of establishing borrowers’ capacity to borrow and to ascertain whether positions are undercollateralized, hence being susceptible to liquidation. Additionally, synthetic asset platforms rely on price oracles for anchoring the value of tokens to real-world assets, while automated market makers (AMMs) make use of price oracles to concentrate liquidity at the current market price, thereby enhancing capital efficiency.
Dynamic NFTs and Gaming
Oracles play a vital role in facilitating smart contracts to support not only financial use cases but also non-financial use cases, such as dynamic NFTs. These Non-Fungible Tokens possess the ability to alter in appearance, value or distribution, depending on external events such as the time of day or weather. Moreover, compute oracles are utilized to produce verifiable randomness, which in turn assists in assigning randomized traits to NFTs or to select random lucky winners in high-demand NFT drops. The on-chain gaming applications can benefit from verifiable randomness to create more engaging and unpredictable gameplay experiences, like the appearance of unpredicted loot boxes or randomized matchmaking during a tournament.
Insurance
Insurance smart contracts incorporate input oracles in their claims processing to authenticate the existence of insurable events. This technique grants unrestricted utilization of physical sensors, web APIs, satellite imagery, and legal data. Additionally, output oracles enable insurance smart contracts to allocate claim payments across other blockchains or traditional payment networks.
Enterprise
Enterprises can utilize cross-chain oracles as a secure blockchain middleware to link their backend systems to any blockchain network, thus enabling these systems to read and write to any blockchain, perform complex logic, and deploy assets and data across chains and counterparties, all using the same oracle network. This allows institutions to promptly join blockchains that are highly sought after by their counterparties and offer smart contract services that their users demand without dedicating significant time and development resources to integrate with each individual blockchain.
Sustainability
Hybrid smart contracts play a crucial role in advancing environmental sustainability by encouraging participation in green practices through enhanced verification techniques that accurately measure the impact of ecologically sound initiatives. Oracles, as a critical tool, provide smart contracts with environmental data obtained from sensor readings, satellite imagery, and advanced machine learning computation, enabling the smart contracts to dispense rewards to individuals who participate in reforestation and prioritize conscious consumption. Moreover, oracles support innovative carbon credit programs that offset the adverse effects of climate change.
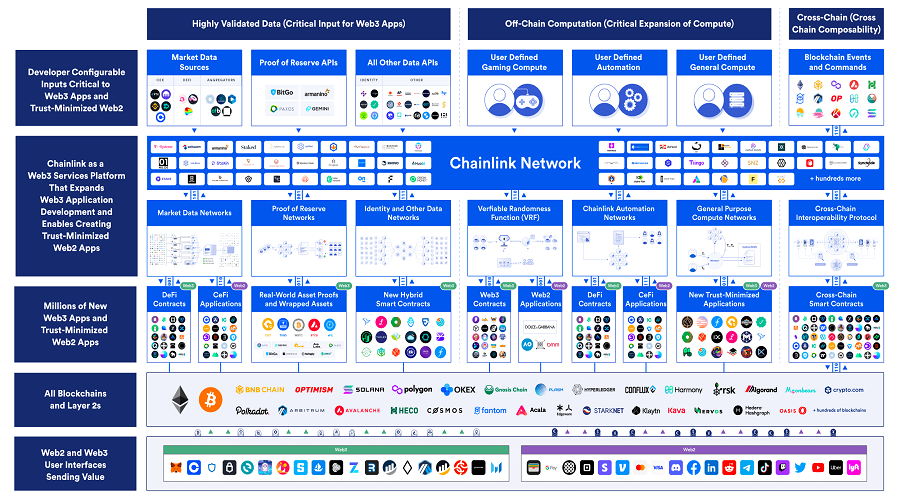
By facilitating access to external resources necessary for leveraging advanced hybrid smart contract use cases beyond basic tokenization, oracles enhance the functionality of blockchain networks. These oracle-powered contracts are akin to the Internet’s revolutionary impact on information exchange, challenging traditional methods of enforcing contractual agreements and exchanging value within society.
Most Popular Blockchain Oracles in 2023
Ensuring efficient operations of smart contracts, the functionalities of blockchain oracles necessitate the identification of popular ones. However, finding the best blockchain oracles can be a confusing and ambiguous task depending on one’s particular requirements. This becomes particularly challenging as multiple blockchain oracles compete for the title of being the most reliable on-chain data source. The process of selecting a suitable blockchain oracle can prove to be a major hurdle for developers and companies. For an overview of the features offered by some of the most popular blockchain oracles in 2023, let us delve into further details.
Chainlink
Chainlink, the largest blockchain oracle on the market, is considered the foremost entry among renowned blockchain oracles. With a market capitalization slightly exceeding $1 billion, Chainlink is a strong player in the blockchain oracle space. Chainlink provides off-chain data to various blockchain-based solutions, including layer 1 blockchains, layer 2 solutions, dApps, and side-chains. This highly regarded blockchain oracle was launched in 2019 with Ethereum as the foundation. It delivers on-chain services to different blockchain platforms such as Compound, Avalanche, and Aave.

Chainlink’s position as an exemplary blockchain oracle is evident from its assuring factor of high security, which is facilitated through its proficient multi-platform functionalities. The platform relies on two formidable features, namely Chainlink Verified Random Function and Chainlink Automation. The former is a protocol that produces a set of random values, complemented with cryptographic proof to ensure authenticity. With the support for unpredictable outcomes, Chainlink VRF protocol enhances the efficacy of smart contracts. Meanwhile, the Chainlink Automation feature caters to maintenance tasks for smart contracts, ensuring seamless execution of operations.
Band Protocol
The compilation of in-demand blockchain oracles set to thrive in the year 2023 would encompass decentralized variants, such as the prominent Band Protocol. This cross-chain oracle operates on the advanced Cosmos ecosystem, housing numerous interoperable networks and providing tamper-proof data feeds for smart contracts through the use of BandChain, the protocol’s public blockchain.

Validators within the BandChain blockchain submit their data requests through APIs or other web sources, subsequently transmitting the gathered data to entities and users. Moreover, the protocol is equipped with the capability of distributing data across diverse blockchain networks via the Inter-Blockchain Communication or IBC protocol of Cosmos.
The explanation of the Band Protocol blockchain oracle’s most noteworthy aspect emphasizes its flexibility in allowing users to create custom oracle scripts to obtain data streams from various external sources in the physical domain. The blockchain network adopts the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism that necessitates validators to stake the BAND coin to retrieve data and validate its genuineness through voting.
Decentralized Information Asset
DIA, or Decentralized Information Asset, is the latest addition to the list of prominent blockchain oracles. The platform is designed specifically for the DeFi landscape and boasts an open-source structure. DIA’s unique approach involves the use of crypto-economic incentives for the dissemination and sharing of transparent price data that is verified by multiple participants. Users are able to customize data feeds by configuring methodologies and sources in accordance with their needs, thereby enabling them to create feeds that are tailored to their specific requirements.

The services of DIA oracle are accessible to users free of charge. This facilitates the verification of price data for financial and digital assets through a community of stakeholders, which ensures the authenticity of data. Additionally, DIA offers scalability advantages to keep up with the ever-changing DeFi landscape. Furthermore, DIA provides oracle services for multiple blockchains, including Ethereum, Fantom, Solana, Avalanche, Polygon, and Arbitrum.
Universal Market Access
UMA is regarded as one of the finest blockchain oracles for developers due to its remarkable effectiveness. This Ethereum-based oracle presents smart contract templates to users, which can be utilized to establish financial smart contracts and synthetic assets. Synthetic financial contracts are digital tokens that resemble real-world assets such as derivatives, and their performance and pricing are tracked using smart contracts. Consequently, investors can now gain exposure to markets where entry barriers are high.

UMA’s platform is highly user-friendly, and it stands out as a viable alternative to blockchain oracles such as Chainlink, thanks to its advanced functionalities. By utilizing UMA’s services, users can easily digitize existing financial products that exist within the real world. UMA’s Universal Market Access oracle serves as a bridge between the DeFi markets and our tangible reality. In addition, UMA is a fully decentralized and open-source oracle, ensuring the validity and reliability of all information sourced.
XYO Network
Notable instances of blockchain oracles encompass XYO network, which provides an array of exceptional services. One need not be concerned with inquiries regarding the mechanics of blockchain oracles when an alternative such as XYO network is available. This Ethereum-driven blockchain oracle protocol utilizes a network of decentralized and anonymous devices to procure precise data about an individual’s or object’s geospatial location. The upshot of this approach is that applications can execute smart contract transactions that necessitate location verification.

The consensus algorithm of XYO Network is the proof-of-origin, which exploits the ‘bound witness’ method for validating the locations of individuals or objects. Significantly, the network incorporates different blockchain oracles, each with unique architectures, to further enhance its operations. This network comprises four crucial physical components that serve different functions, namely sentinels, bridges, diviners, and archivists.
Sentinels function as location witnesses by maintaining ledgers for interim solutions to heuristics. Bridges are responsible for interpreting geospatial data and transmitting the information to archivists via sentinels. Diviners are the tools utilized for analyzing problem-solving techniques. Archivists play a crucial role in storing data obtained from bridges and providing the data to diviners. This streamlined system ensures smooth data flow and efficient problem-solving in a professional and formal capacity.
Tellor
One notable example of a blockchain oracle currently present in the blockchain landscape is Tellor. Being a permissionless oracle, it enables dApps operating in diverse industries to obtain access to off-chain data. The roots of Tellor can be traced back to its association with Daxia, which is a derivatives platform based on Ethereum.

The Tellor blockchain oracle employs a reporting client as its central component to carry out its functions. This reporting client supports a network of reporters who undertake the critical tasks of searching, querying, verifying, and validating data. The Tellor oracle protocol is distinguished by two types of data feeds: Spot Price and Custom Price. Spot Price offers market data which is sourced from existing APIs, while Custom Price enables data modification to suit specific client needs.
DOS Network
Another blockchain oracle that has gained popularity amongst the leading ones is the DOS Network. This network functions as a decentralized oracle on layer 2 and facilitates multiple mainstream blockchain networks. The most remarkable advantage of the DOS Network lies in its ability to provide accurate and up-to-date real-time data feeds. This feature enables the network to connect smart contracts and dApps to trustworthy data sources, resulting in faster processing and added benefits.

The promptness with which the DOS network furnishes oracle data is a prominent feature that is particularly noteworthy for smart contract applications that demand immediate attention. The DOS network has the ability to finalize off-chain transactions in a mere matter of one second. However, it ought to be remembered that the performance capabilities of the DOS network are hindered by the operational constraints of layer 1 protocols.
Nest Protocol
Described as a truly decentralized oracle, the Ethereum-based Nest protocol presents a significant option in the realm of blockchain oracles. Its reliability is reinforced by a reference system, known as quotation mining, which guarantees the correctness of off-chain information. Consequently, the Nest protocol has the capability of providing a transparent oracle process, with the participation of three key network participants: price callers, miners, and verifiers.
The Probabilistic Virtual Machine (PVM) in conjunction with the Nest protocol is available for developers to utilize. This virtual machine possesses comparable functionalities to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), including a range of basic functions and on-chain assets within its library. Additionally, the Nest protocol functions on the native NEST token, which provides the necessary power for the oracle’s ecosystem and furnishes economic incentives for participants network-wide.
iExec RLC
iExec is a well-known option for blockchain oracles within the DeFi sector. It distinguishes itself from typical responses to the question “How do blockchain oracles function?” through its provision of a cloud computing services marketplace. These services, accessible through the iExec marketplace, facilitate the bridging of web2 applications and businesses with web3 technology.

The DeFi oracle offers an array of convenient Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that facilitate the creation of personalized oracles for web3 applications. Not only that, but users also have the option of renting out their computing services while still holding possession of the respective assets.
API3
The compilation of top-performing blockchain oracles includes API3, a decentralized oracle facilitating the integration of web3 applications with off-chain data streams. API3 serves as a valuable tool for collecting information from diverse markets, including cryptocurrencies, stocks, and commodities. The most noteworthy aspect of API3 is its utilization of decentralized APIs to access data feeds directly from primary sources.

API3 boasts a noteworthy characteristic with respect to its web3 middleware, known as Airnode, which facilitates the establishment of a direct link between blockchain applications and web Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). Consequently, Airnode promotes the seamless compatibility of blockchain technology with any API. Notably, prominent blockchain networks such as Polygon and Fantom are exemplary beneficiaries of API3.
What is Yield Farming? Gain a comprehensive understanding of the terminology associated with Yield Farming
The concept of Yield Farming, prominent Yield Farming platforms, and the associated risks and opportunities are explored in this article,...
Read moreWhat is Initial DEX Offering (IDO crypto)? Does playing IDO really give you a 100% chance of winning?
One may inquire as to why the Initial DEX Offering (IDO) has gained widespread popularity and whether investing in IDO...
Read moreWhat is ERC – 20? Advantages, disadvantages & how to create ERC- 20 network tokens
In this article, we will explore ERC-20 and ERC-20 tokens along with their applications and advantages and disadvantages. For those...
Read moreWhat is Airdrop Crypto? Instructions for making airdrop coins in the Crypto market
What is Airdrop and how many forms of Airdrop Crypto exist? Discover the limitations and effective instructions on how to...
Read moreWhat is DAO? Limitations and Investment Potential of DAO in Crypto
Understanding the terminologies used in the field of cryptocurrency is crucial for individuals involved in Crypto market participation or intending...
Read moreWhat is zkEVM? Classification of groups zkEVM
ZkEVM is an abbreviation for the term "Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine". It is a protocol that enables the execution of...
Read moreWhat is web3 technology? How to invest in Web3 in 2023
The emergence of Web 3.0 following Web 2.0 has brought about increased flexibility and superior interaction capabilities compared to its...
Read moreWhat is move to earn? best move to earn crypto in 2023
In the current GameFi market, it is possible to combine the seemingly unrelated tasks of earning money and improving one's...
Read moreWhat does NFT crypto stand for: Clarifying the Significance of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) through technical examination
Non-fungible token (NFT) art are digital assets stored on a blockchain that depict physical or non-physical items, such as digital...
Read moreWhat are play to earn (P2E) Games? How to earn money with play game crypto?
Play to Earn has emerged as a popular trend in mid-2021, leading to a notable increase in the activity of...
Read moreWhat is an oracle in blockchain? Top blockchain oracle projects 2023
The intended function of blockchain technology was never to operate in isolation from the larger economic ecosystem. Despite the challenges...
Read moreBinance account sign up: What is binance account? how to create binance account?
Numerous cryptocurrencies are supported by Binance and its proficiency in ensuring swift exchange operations between volatile coins and fiat currencies...
Read moreWhat is a defining feature of the Metaverse Crypto? What does the term Metaverse refer to?
We have heard numerous prominent figures, such as Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook, and Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, expound...
Read moreWhat are AI Tokens? Best AI Coins & Tokens to Invest in
The predicted impact of artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to revolutionize various sectors, including the field of cryptocurrency. The AI...
Read moreWhat are Fan Tokens? How Binance Fan Tokens are Revolutionizing the World of Sports and Entertainment?
The Fan Token is a term that has been shared by the CEO of the cryptocurrency exchange CZ on Twitter,...
Read more