The Chainlink crypto (LINK) is an infrastructure project that encompasses multiple sub-products, such as Data Feed, VRF, Functions, CCIP, and Automations. These features enable projects within the market to construct and advance in the DeFi and Web3 space.
The Chainlink project was initially introduced in September 2017 with the aim of resolving the “Oracle problem” associated with Blockchain technology.
Smart contracts are unable to interact with any external data sources outside of Blockchain. Therefore, in order to expand the applicability of smart contracts, a bridging mechanism is necessary to connect them with external data sources within Blockchain. However, these data sources cannot come from a centralized entity because if the data source connected to the smart contract is controlled, then the smart contract itself will also be controlled. This goes against the fundamental nature of Blockchain.
What is Chainlink and how can it address this issue? Let us delve into this topic together through this article.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Chainlink Crypto?
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that allows smart contracts to safely interact with real-world data and services outside of blockchain networks. With Chainlink, traditional systems currently powering modern economies can seamlessly connect with the blockchain industry, providing increased security, efficiency, and transparency in business and societal processes.

Oracle has made an announcement regarding the provision of real-time data such as market prices, commodity locations, and other information to smart contracts. In the absence of such infrastructure provided by Oracle on Blockchain layer 1. It would be impossible for programmers to develop applications such as DeFi and Insurance on that Blockchain (due to the unavailability of data about prices and external information on the chain).
However, since the introduction of subsequent products such as VRF, Automations, CCIP, etc., Chainlink has gradually expanded into an infrastructure project rather than solely an oracle. The article presented below will provide comprehensive information on Chainlink for interested readers.
Chainlink’s products
At present, Chainlink provides 6 products that function as foundational infrastructure for projects, which include:

Chainlink Data Feeds offer a secure and reliable source of data for smart contracts in the DeFi space. This feature has been utilized by numerous projects including Aave, Compound, TraderJoe, and Synthetix. These data feeds aggregate information from major players in the industry such as Binance, CoinMarketCap, and CoinGecko.
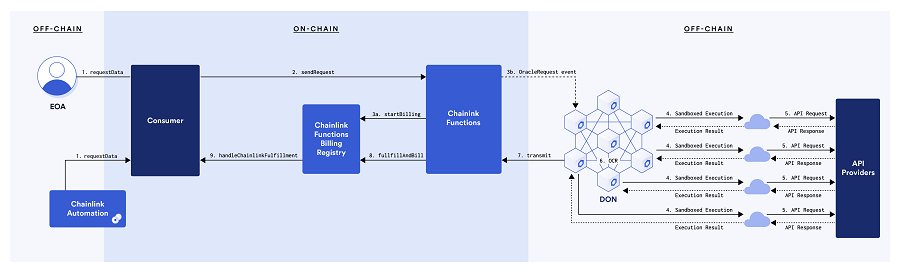
Chainlink Functions
The Chainlink Functions is a serverless Web3 development platform that enables users to access any data from any API and perform custom computing on the secure and reliable network of Chainlink.
The latest product from Chainlink has already been adopted by several partners such as Dopex, Playground, Thirdweb, BlockScholes, to name a few.
Chainlink Automation
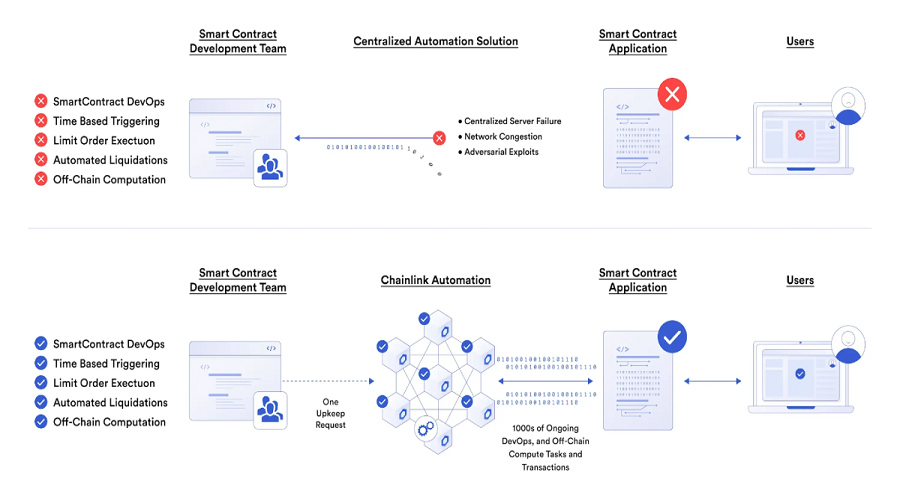
Chainlink Automation enables Web3 developers to automate functions of smart contracts through a set of tools that allow developers to build automated workflows triggered by external events or conditions, such as changes in asset prices, completion of payments, or the occurrence of a specific date or time. The provided toolkit enriches the developer experience by facilitating the seamless integration of Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network, ensuring secure, reliable, and efficient automation of smart contracts.
At present, Automations is being employed by projects such as StakeDAO, Pancakeswap, and others for various purposes.
Chainlink VRF
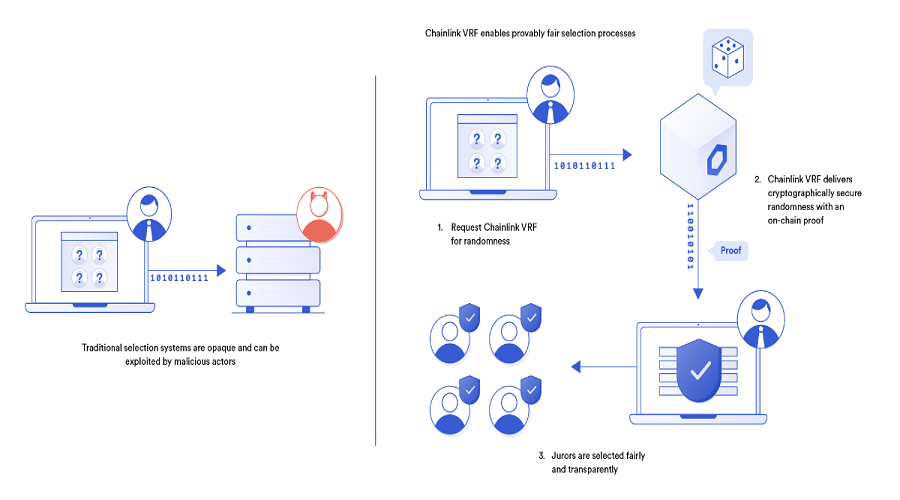
With Chainlink VRF, developers can generate random numbers that can be verified on the blockchain, ensuring that the results are not susceptible to tampering or bias in any way. This feature is particularly beneficial for applications that require randomness, such as games, lotteries, and gambling.
Currently, VRF is being utilized by prominent projects such as Axie Infinity, PoolTogether, and Aavegotchi, among others.
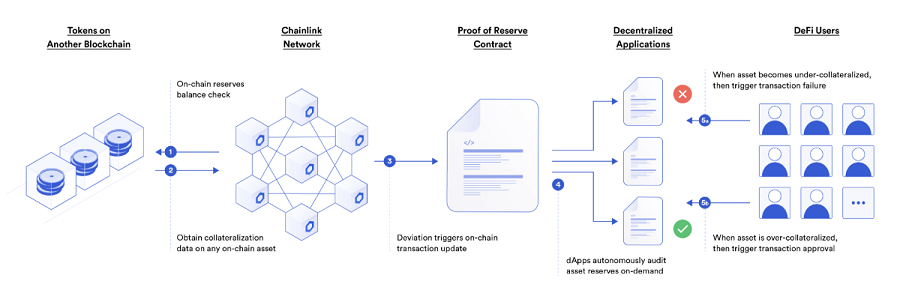
Chainlink Proof of Reserve
Chainlink’s Proof of Reserve feature enables transparent and timely monitoring of asset reserves. Users can verify that a specific asset, such as a stablecoin, is fully backed by the reserve of the underlying asset, such as USD. This ensures that reserve assets are always held securely, providing greater peace of mind for investors and traders alike.
Recently, the Proof of Reserve feature has been regarded as the standard for CEX exchanges after FTX and numerous others experienced collapse. This feature is also employed by major players such as Paxos, BitGo, TrustToken, among others.
Cross-chain Communication (CCIP)
The Cross-Chain Interaction Protocol (CCIP) provides an open standard for developers to build decentralized services and applications that can send messages, exchange tokens, and initiate actions across multiple blockchain networks. This fosters greater interaction and scalability of blockchain applications.
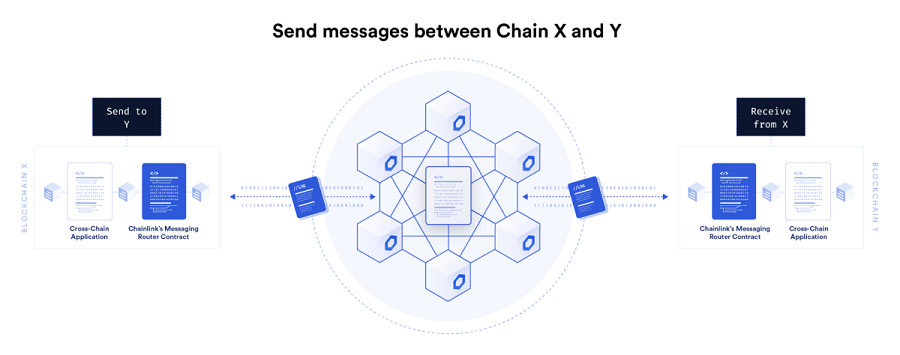
Currently, CCIP has become widely utilized by Cross-chain bridges and Cross-chain messaging. Additionally, CCIP possesses the capability to unlock new functionalities for decentralized applications. One example is allowing users to pledge collateral in chain A while still being able to borrow funds from chain B, due to the established interaction between the two chains.
How does Chainlink crypto work?
What makes Chainlink stand out is their ability to obtain data from Oracles and inject it into the Blockchain in a decentralized manner.
The solution offered by Chainlink presents opportunities for smart contracts to handle secure payments, financial agreements, legal documentation, trade between parties, and countless other potential applications in the future.
A network within a network constitutes a complex framework
Within the ecosystem of Blockchain, a node refers to any computing device that is connected to the network. These nodes verify transactions, and Chainlink utilizes a set of independent “nodes” to collect data from various Oracle sources.
For instance, one node has the capability to connect with national weather services, while another node can establish connections with the New York Stock Exchange.
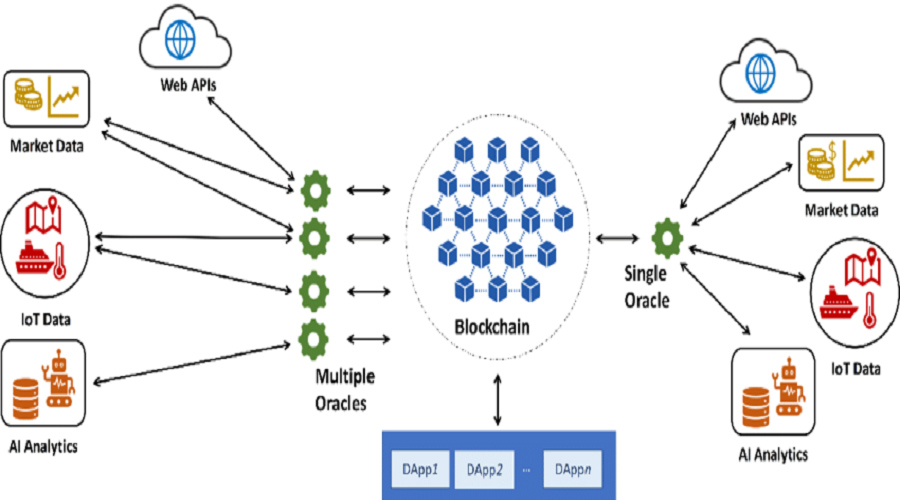
The structure of the Chainlink network enables it to provide a diverse range of Oracle services in a consistent manner. In contrast to blockchains that operate as a single monolithic network with a unified consensus mechanism. The Chainlink Network is decentralized, formed from multiple independent Oracle networks that run on the same software but operate independently of each other.
By choosing such a design, Chainlink is able to horizontally scale up its operations, as any number of Oracle networks can function in parallel without being dependent on any other Oracle network. Each Oracle network can have the autonomy to determine:
- How many independent Oracles participated in the event?
- Where does the Oracle source data come from and what computations are performed by the Oracle network?
- The security measures employed to safeguard data and the frequency with which data is supplied along the chain are both significant factors.
Chainlink employs multiple APIs and nodes to prevent fraudulent activities, comparing their results to ensure accuracy. Afterward, Chainlink automatically processes and sends data requests to the smart contract. The Oracle-enabled smart contract will compensate the submitted data with LINK tokens as a fee for their services.
Furthermore, in order to render fraudulent activities virtually impossible for malicious actors, Chainlink may mandate node operators to utilize LINK tokens as collateral. Sanctions for providing inaccurate data will compel them to abandon their intentions.
Chainlink’s Onchain Architecture
Chainlink nodes, as an Oracle service, provide responses to data query requests made by or on behalf of user contracts (referred to as request contracts).
Chainlink comprises of three core smart contracts within its blockchain that run behind the user interface
- Reputation contract: It is imperative to monitor the operational metrics of the Oracle service provider as a part of maintaining an efficient and effective IT infrastructure.
- Order-matchmaking contract: The proposed Service Level Agreement (SLA) was implemented by recording the SLA metrics and collecting bids from Oracle vendors. Following this, the most appropriate bid was chosen using a reputable contract and the SLA with Oracle was successfully fulfilled. This was carried out with a professional and formal approach.
- Aggregating contract: The feedback from Oracle suppliers was collected and the final overall result of the Chainlink query was computed. Additionally, the data from the Oracle suppliers was furnished back to the reputable contract.
Quy trình làm việc onchain của chainlink có 3 bước:
- Select Oracle;
- Data reporting;
- Summary of results.
Chainlink’s Offchain Architecture
The processing of standard blockchain interactions, scheduling, and integration with external shared resources is facilitated by the utilization of Chainlink Core, which is a standard open-source implementation that supports various Chainlink nodes.
Node operators have the option to incorporate additional software extensions, known as external adapters, which offer supplementary services beyond the dedicated blockchain.
The Adapter is an external service that models itself as a service-oriented architecture. By adopting this approach, any program written in any programming language can conveniently implement this service by adding intermediate small APIs in front of them.
Chainlink’s Security
Chainlink has implemented several measures to ensure the integrity of its services.
Mortgage insurance: In the context of smart contracts, the owner may require a node to pledge its assets (LINK tokens) to ensure the completion of a task. Failure to provide the required data would result in the forfeiture of the deposit to the contract owner.
Decentralized approach: One way to address a single faulty source is by obtaining data from multiple sources. Chainlink implements this approach through the utilization of multiple nodes and data sources to facilitate smart contracts.
Trusted hardware: The reliable hardware has been designed to prevent tampering and resist direct physical access by adversaries. This method has also been utilized by Chainlink to further enhance its approach to decentralized access.
In order to achieve reliable execution goals, Chainlink has acquired a specialized hardware device called Town Crier. This proprietary device, developed by Ari Juels, a computer science professor at Cornell University, serves as a “Trusted hardware” and is designated as a technical advisor for Chainlink.
Chainlink’s Security Service
These systems and services provide additional security to the chainlink platform and its users.
Authentication system: By monitoring the behavior of Oracles on the chain, it is possible to provide objective performance indicators that can guide users in their decision-making process.
Reputation point system: The recording and publication of user rankings regarding vendors and nodes, coupled with the provision of means for users to evaluate Oracle’s performance, constitute a fundamental component of the chain. This ranking information is readily available for reference in other smart contracts.
Certification service: Issuing high-quality assurance from Oracle suppliers.
Contract upgrade service: A service option is made available to users, which empowers them to manage erroneous smart contracts.
Detailed information about LINK token
LINK Key Metrics
- Ticker: LINK
- Decimals: 18
- Blockchain: Ethereum, BNB Chain, Fantom, Solana, Optimism, Arbitrum, Avalanche C Chain, HECO, Gnosis, Polygon, Sora, Terra, Near.
- Token type: Utility Token.
- Token Standard: ERC-677 (cải tiến từ ERC-20).
- Total Supply: 1,000,000,000 LINK.
- Circulating Supply: 517,099,970 LINK (52/100%).
- Ethereum Contract: 0x514910771af9ca656af840dff83e8264ecf986ca
- BNB Chain Contract: 0xf8a0bf9cf54bb92f17374d9e9a321e6a111a51bd
- Solana Contract: CWE8jPTUYhdCTZYWPTe1o5DFqfdjzWKc9WKz6rSjQUdG
- Fantom Contract: 0xb3654dc3D10Ea7645f8319668E8F54d2574FBdC8
- Polygon Contract: 0x53e0bca35ec356bd5dddfebbd1fc0fd03fabad39
- Avalanche C-Chain Contract: 0x5947bb275c521040051d82396192181b413227a3
- Optimism Contract: 0x350a791bfc2c21f9ed5d10980dad2e2638ffa7f6
- Arbitrum Contract: 0xf97f4df75117a78c1A5a0DBb814Af92458539FB4
If Bitcoin has its smallest unit called satoshi, LINK also has its smallest unit called Juel. The conversion rate is 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 (1e18) Juel for 1 LINK.
LINK Token Allocation
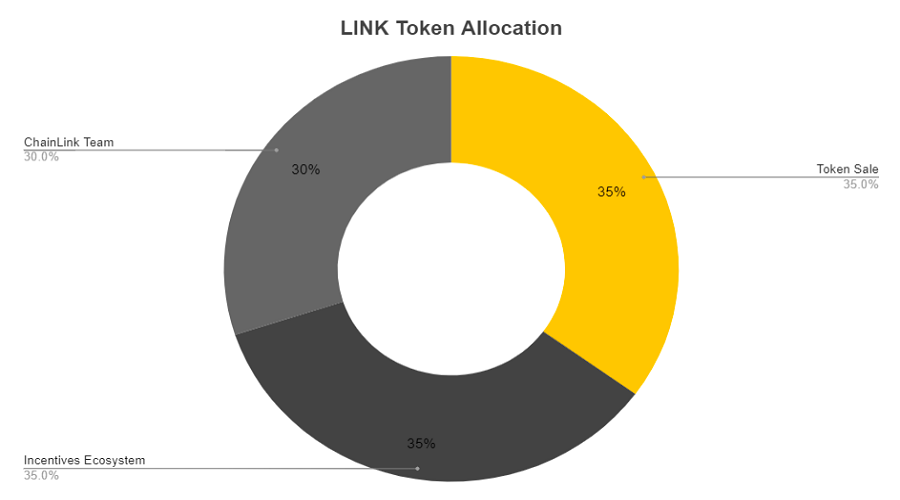
Chainlink’s total supply will be
- 35% sold in token sale
- 35% for Node Operator Incentives
- 30% is held by Chainlink Team
LINK Token Release Schedule

LINK Token Use Cases
LINK is the native cryptocurrency of the Chainlink network and has several applications that are being utilized such as the following:
- Pay: LINK serves as a payment method for services within the Chainlink network. Additionally, data providers receive rewards in the form of LINK.
- Stake: In order to furnish appropriate data to the network, data providers are required to stake a certain amount of LINK to ensure the accuracy of their data provision. It should be noted that in the event of deliberate sabotage, data providers will be penalized and have their staked LINK deduction.
- Administration: Những người nắm giữ LINK có thể tham gia vào quản trị của mạng lưới Chainlink. Họ có thể bỏ phiếu cho các đề xuất để thay đổi các thông số mạng hoặc thêm tính năng mới.
- Mortgage & Liquidity Provision: LINK có thể được sử dụng làm tài sản thế chấp và cung cấp thanh khoản trong các ứng dụng tài chính phi tập trung (DeFi) như Aave và các sàn DEX.
In general, the LINK currency plays a crucial role in the Chainlink ecosystem, allowing the network to provide highly reliable and decentralized oracle services for smart contracts and other blockchain applications.
LINK Token Sale
The initial coin offering (ICO) for Chainlink was conducted during the period of September 17th to September 20th in the year 2017. During this fundraising event, a total of 350 million LINK tokens (equivalent to 35% of the total supply) were sold, raising a sum of 32 million US dollars. The tokens were sold at prices ranging from 0.09 to 0.11 US dollars per token.
LINK Token Exchange & Wallet
Ví lưu trữ LINK Token
As LINK is an ERC-20 token, it will be stored on Coin98 Wallet using the following steps for secure storage:
- Step 1: At the main interface, select Receive.
- Step 2: Enter LINK in the search box.
- Step 3: Copy the LINK ERC-20 wallet address and send the LINK token to this address.
LINK Token Exchange
The LINK token has the potential to be traded on both decentralized and centralized exchanges. Below are some high-liquidity exchanges that traders should consider utilizing to avoid any slippages in price.
- CEX: Binance, Coinbase, Kucoin, Kraken, Bitfinex, Bithumb, Bitstamp.
- DEX: Uniswap (Ethereum, Polygon, Optimism), Spookyswap (Fantom), TraderJoe (Avalanche), Pancakeswap (BNB Chain),…
Project team, investors, partners Chainlink Crypto
Project team
The Chainlink team is a highly experienced group with a diverse skill set across various industries. The following are some notable members of the Chainlink team:
- Sergey Nazarov is the CEO and co-founder of various famous business ventures such as Smart Contract, Secure Asset Exchange, and CryptoMail which is a decentralized email service. He is well-known for pioneering these projects in the field of blockchain technology.
- Steve Ellis is the Chief Technology Officer and co-founder who previously served as a software engineer at Pivotal Labs and Secure Asset Exchange.
- Mr. Rory Piant holds the position of Business Director within our organization.
- Ari Juels serves as a scientific advisor, providing valuable insights and guidance in his area of expertise.
- Mr. Dan Kochis is serving as the Product Manager.
- Mr. Thomas Hodges is the Marketing Director.
- Andy Boyan holds the position of Chief Financial Officer, signifying his responsibility for overseeing and managing the financial operations of the company.
- John Redgrave serves as the Technical Director of the company.
- Johann Eid serves as the Director of Products, responsible for overseeing the development and launch of the company’s product offerings.
This is just a sample and the Chainlink team has many other members. Each team member possesses high levels of expertise and professionalism in their respective fields, making significant contributions towards the development of the Chainlink platform.

Furthermore, Chainlink boasts a team of highly acclaimed and experienced advisors in the field of blockchain and financial technology. Below are some of the prominent Chainlink advisors:
- Ari Juels is a computer science professor at Cornell University and currently serves as a scientific advisor to Chainlink.
- Andrew Miller is a professor at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and serves as a security advisor for Chainlink.
- Tom Gonser is the founder of DocuSign, an enterprise that specializes in e-signatures.
- Balaji Srinivasan previously held the position of Chief Technology Officer at Coinbase and has served as a co-partner at Andreessen Horowitz (a16z).
Investors
In September 2017, Chainlink successfully raised 32 million USD for its development team through a Pre-sale and Initial Coin Offering, according to data from Crunchbase.
Partner
In the Crypto market, Chainlink may have the largest number of partners due to the scope of their field, which includes traditional markets, CeFi, and DeFi. Therefore, it is possible to categorize Chainlink’s partners into several areas.
- Blockchain: Ethereum, BNB Chain, Solana, Polygon, Avalanche, Arbitrum, Optimism, Fantom, Klaytn, Metis, Moonbeam, Moonriver, HECO, Harmony, Gnosis,…
- DeFi: Uniswap, Aave, Compound, Beefy Finance, Coin98, Metamask, Pancakeswap,…
- Công ty truyền thống: SWIFT, Google, Oracle, Intel, Microsoft,…
Chainlink has amassed a vast ecosystem of partners, numbering in the thousands. For your convenience, you may peruse our website to discover which projects utilize Chainlink’s innovative technology.

Roadmaps & Updates
The following presents a list of significant milestones that Chainlink has achieved up until the present time.
- September 2017: Chainlink was founded by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis.
- September 2017: Chainlink conducted an ICO (Initial Coin Offering) raising about 32 million USD and was listed on Binance shortly after.
- June 2019: Chainlink cooperates with Google Cloud to provide solutions for the implementation of blockchain systems in enterprises.
- June 2019: Chainlink is listed on Coinbase Pro exchange.
- March 2020: Chainlink launches Keepers feature (renamed Automation), allowing developers to take action automatically when conditions are met.
- May 2020: Chainlink introduces a VRF (Verifiable Random Function) feature that allows blockchain-based applications to generate verifiable random numbers.
- July 2020: Chainlink integrates with blockchain insurance company Etherisc to create a weather insurance solution.
- September 2020: Chainlink introduces Price Reference Data feature to provide accurate price data for blockchain applications.
- August 2020: Chainlink helps in implementing a weather monitoring system for Senegal through a partnership with Oracle and Microsoft.2/2021: Chainlink introduces Off-Chain Reporting (OCR) feature to improve the security and reliability of data reports from external sources.
- April 2021: Chainlink publishes Whitepaper 2.0 to decentralize the network and help Chainlink become the Oracle with the most diverse data in the market.
- August 2021: Launch of the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) product that enables tokens and information to move between blockchains.
- September 2022: Announced Chainlink BUILD and Chainlink SCALE programs to help projects access Chainlink’s diverse data, LINK stakers can provide data and create a premise for Chainlink Economics 2.0
- 3/2023: Announcement of product launch Functions – This is a product that allows smart contracts to connect and use data from Web2 APIs easily.
What is CCIP?
On the 17th of July, Chainlink made an official announcement about the release of its Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), a solution aimed at enhancing connectivity between different blockchain networks.
The CCIP was created as a replacement for traditional Cross-Chain Bridges in order to facilitate rapid, secure and cost-effective asset interactions between various blockchain networks. This solution offers superior efficacy at a reduced cost compared to its predecessors.
The CCIP solution not only resolves the limitations of the Cross-Chain Bridge, such as vulnerability to hacking, high costs and long waiting times, but also enhances the overall interactivity between blockchain networks in a smooth and secure manner.
Utilizing the token LINK as a gas fee in the CCIP not only enhances its functionality within the Chainlink ecosystem but also increases its practicality.
Furthermore, on July 20th, CCIP will also be made available to developers on testing networks such as Arbitrum Goerli, Avalanche Fuji, Ethereum Sepolia, Optimism Goerli, and Polygon Mumbai.
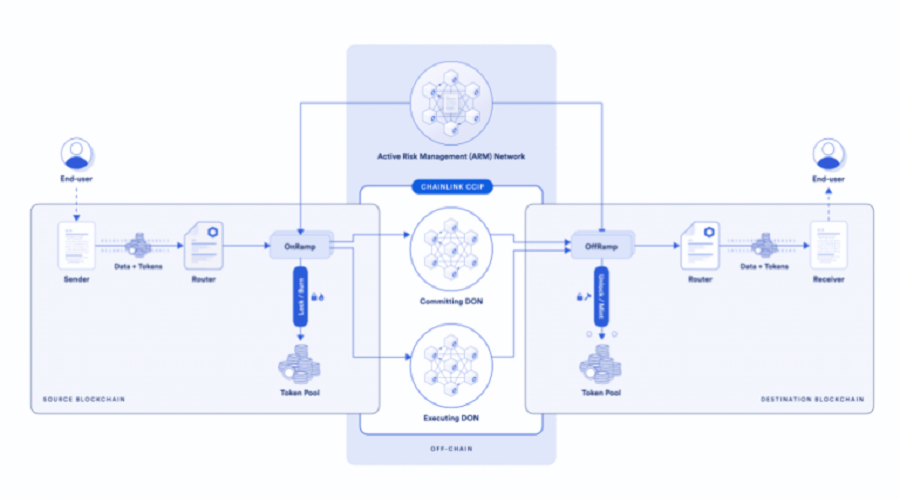
What is Cross-chain Bridge?
The cross-chain bridge is an essential solution for connecting various blockchain chains, enabling them to interact and exchange assets with each other, essentially acting as a bridge between different chains.
Blockchain ecosystems often exist as independent entities with their own unique structure and protocol, which makes it challenging to connect and exchange information. Hence, the cross-chain bridge plays a crucial role in linking different blockchain networks together.
Applications of CCIP
When utilizing CCIP to convert ETH from the Ethereum blockchain to the Optimism blockchain, it is possible to implement a range of automated transactions and customized purposes for utilizing ETH on the Optimism blockchain. The utilization of CCIP serves as a valuable tool for streamlining the process of transferring ETH between blockchains and enables the execution of tailor-made functions on the Optimism blockchain, based on unique user requirements and preferences.
For instance, if one wishes to transfer ETH from the Ethereum chain to the Optimism chain through the CCIP protocol, the following steps can be taken in order to execute the transaction:
- Interaction with Cross-Chain Bridge: To begin with, we will utilize CCIP to establish connectivity and facilitate interaction with the Cross-Chain Bridge between the Ethereum chain and Optimism chain. This process will ensure the secure and reliable exchange of assets between the two chains.
- Automatically swap ETH to Optimism ETH (OETH): After the successful conversion of ETH to the Optimism chain, it is possible to utilize an automatic swap protocol to convert the tokens into Optimism ETH (OETH) to ensure that the assets remain in line with the standards and structure of the Optimism chain.
- Use OETH for custom purposes: With OETH being received on the Optimism chain, there is now the ability to customize its utilization. For instance, OETH can be utilized to participate in the DeFi network on the Optimism chain, invest in projects, or participate in other financial activities available on this chain.
Additionally, CCIP offers various applications tailored to meet different needs and purposes such as:
- Cross-chain Lending: It is feasible to employ collateral tokens on Blockchain A in order to secure stablecoins from Blockchain B. To provide an example, with the assistance of the ETH token on the Arbitrum platform, one can obtain stablecoins from the Ethereum chain, thus facilitating transactions and investments without the need to transfer tokens to alternative chains.
- Cross-chain NFT: CCIP facilitates the creation and minting of NFTs on one blockchain A, followed by receiving the NFT on another blockchain B. This enables the interconnectivity of the NFT ecosystem across multiple blockchains and facilitates convenient transactions and usage of NFTs on diverse platforms.
- Cross-chain LST: The CCIP facilitates the connection of liquidity tokens between different blockchain networks, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of various DeFi platforms across different chains. For example, users can stake ETH tokens on the ERC network and earn profits from staking on the Arbitrum chain without leaving the original blockchain network.
One point to note is that all transactions made will be paid in $LINK tokens.
Notable projects
Aave

BGD Labs is currently in the process of integrating CCIP into Aave, a renowned DeFi protocol, with the aim of bolstering its cross-chain administration system. The integration will facilitate Aave’s expansion into new networks, enabling seamless integration between chains while optimizing gas costs.
Moreover, the objective behind this effort is to facilitate favorable conditions for Aave’s cross-chain management system, enabling simplified operations and providing comprehensive decentralized financial services to users.
Synthetix
Through the initial integration of Chainlink CCIP, Synthetix has the capability to generate a shared pool of synthetic assets across multiple blockchains

Synthetix Teleporters utilize CCIP for token conversion, which includes mint/burn mechanisms, enabling the burning of assets on the source network and their creation on the destination network, ensuring the stable maintenance of sUSD’s overall supply without the need for two versions of the same asset to be guaranteed.
In the future, Synthetix has the potential to expand the functionality of the Synth Teleporter to allow cross-chain compatibility with additional EVM-compatible chains, including Arbitrum and Base.
Synthetix is also conducting research on the implementation of Chainlink CCIP for supplementary use cases, which includes perpetual cross-chain synthetic futures contracts, cross-chain staking pools, and other applicable use cases.
Current opinion
The ongoing Layer 2 battle is proving to be highly engaging, encompassing not only the transfer of funds between networks, but also a demand for utilizing surplus liquidity across various network layers, including both Layer 1 and Layer 2. In this trend, CCIP is truly a noteworthy product, and I firmly believe that it will enjoy widespread adoption in the future due to the economic advantages it offers.
The CCIP not only expands the DeFi market but also drives competition in the Omnichain realm. The applicability of CCIP and the high level of competition arising from the Omnichain Token standard and infrastructure of LayerZero are significant factors that provide CCIP with a comparative advantage over other solutions such as Circle.
One noteworthy aspect of CCIP is the 10% reduction in transaction fees when paying with LINK compared to other Gas Tokens. This incentive encourages users to hold LINK for a longer period while also transferring a portion of the fee to those who participate in Staking LINK on the Oracle network.
I am of the opinion that CCIP is a popular product with considerable potential for future application. Its superior features and high competitiveness make it an attractive choice for the DeFi market and offer significant benefits to both users and developers.
What is Octopus Network (OCT) ? A comprehensive overview of the OCT cryptocurrency
The NEAR Protocol currently hosts an immensely significant project for its ecosystem, which regrettably has yet to garner the attention...
Read moreWhat is Yield Farming? Gain a comprehensive understanding of the terminology associated with Yield Farming
The concept of Yield Farming, prominent Yield Farming platforms, and the associated risks and opportunities are explored in this article,...
Read moreWhat is Ripple ( XRP coin )? An general introduction to the Ripple coin
Bitcoin is the largest digital currency in the world, with a limit of 21 million units, and it is well-known...
Read moreWhat is Initial DEX Offering (IDO crypto)? Does playing IDO really give you a 100% chance of winning?
One may inquire as to why the Initial DEX Offering (IDO) has gained widespread popularity and whether investing in IDO...
Read moreWhat is ERC – 20? Advantages, disadvantages & how to create ERC- 20 network tokens
In this article, we will explore ERC-20 and ERC-20 tokens along with their applications and advantages and disadvantages. For those...
Read moreWhat is Airdrop Crypto? Instructions for making airdrop coins in the Crypto market
What is Airdrop and how many forms of Airdrop Crypto exist? Discover the limitations and effective instructions on how to...
Read moreWhat is Venom Network? It is the first blockchain to be monitored by the UAE regulatory authorities
What is Venom? Venom Network is the UAE's (United Arab Emirates) first Blockchain project initiated by the International Financial Center....
Read moreWhat is DAO? Limitations and Investment Potential of DAO in Crypto
Understanding the terminologies used in the field of cryptocurrency is crucial for individuals involved in Crypto market participation or intending...
Read moreWhat is Mina Protocol (MINA)? Complete set of cryptocurrency MINA Token
The blockchain platform, Mina, has garnered significant attention from users for a considerable period, having been sold on Coinlist. Furthermore,...
Read moreWhat is Injective Protocol (INJ)? All you need to know about INJ coin
Injective was initially introduced in October 2020 as a cross-chain protocol. Since June 2021, the project has evolved into a...
Read moreWhat is Sui Crypto? Details About SUI Token
The emergence of Sui blockchain has brought forth a new generation of blockchain technology. Its groundbreaking features and notable advantages...
Read moreWhat is Polygon zkEVM? Layer 2 zkEVM is a class rival of zkSync
On March 27, 2023, Polygon zkEVM was officially launched on Mainnet Beta, joining the ranks of other prominent Layer zkEVM...
Read moreWhat is StarkNet Crypto? StarkNet Ecosystem Overview
Inquiring about the ecosystem of StarkNet crypto, we seek information on its various components and current development phase. Furthermore, we...
Read moreWhat is Astar Network & Shiden Network? Complete set of ASTR, SDN Token
This article will provide comprehensive information on Astar Network and Shiden Network, including their prominent features and tokenomics details of...
Read moreWhat is Gnosis Crypto (GNO)? Complete set of GNO Cryptocurrency
What is Gnosis Crypto (GNO)? This article provides comprehensive and valuable information regarding the digital currency Gnosis (GNO) for individuals...
Read more