The emergence of Web 3.0 following Web 2.0 has brought about increased flexibility and superior interaction capabilities compared to its predecessors. It is expected that Web 3.0 technology will inevitably become a trend and dominate the internet market in the future. This presents a significant opportunity, particularly for those who have an interest in this new programming field. For more detailed information on what Web3 is, visit 247BTC.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is web3 technology?
The third generation of Internet services, commonly referred to as Web 3.0 or web3, has emerged as a decentralized network that connects data in a personalized and faster way for users. Web 3.0 is supported by advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and semantic web, along with blockchain security measures to ensure safe and secure information sharing.
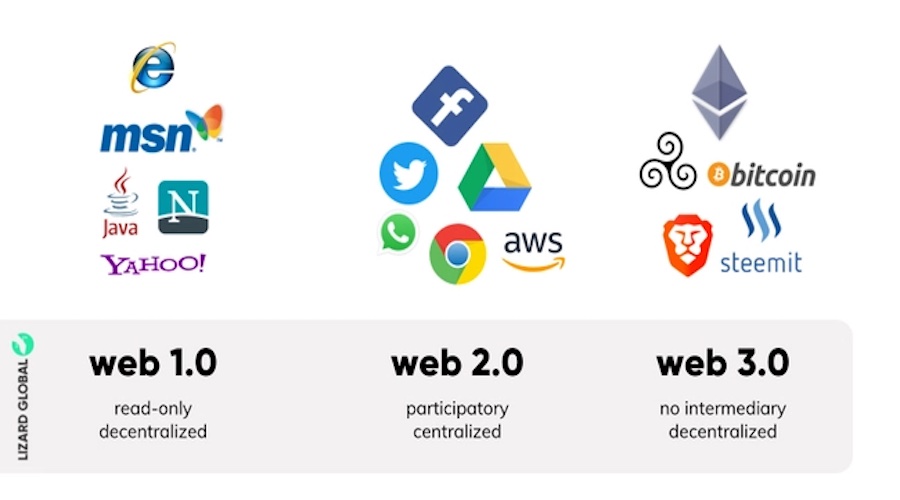
At present, the web is static and cannot be customized according to the individual needs of users. Web 3.0, an advanced version of Web 2.0, promises to be more flexible and interactive. Through the implementation of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology, Web 3.0 will redefine the web experience with structural changes aimed at enhancing user experience.
In Web 3.0, data is securely stored and distributed across multiple devices, eliminating the need for centralized servers. This design also reduces the risk of large-scale data breaches, as data is no longer stored in a centralized location, making it more flexible and less vulnerable to compromise.
Main Features of Web 3.0
- Open – The software was created utilizing an open-source system that was developed by a pre-existing and transparent community of developers. Moreover, it underwent extensive refinement and optimization under the full scrutiny of the public gaze.
- Trustless – The network offers users the liberty to engage in public and private interactions without intermediaries, exposing them to potential risks, thereby rendering the data unreliable.
- Permissionless – Individuals and suppliers are welcome to participate without the need for permission from the controlling entity.
- Ubiquitous – Web 3.0 will provide pervasive Internet access to all individuals, irrespective of their location or time. The limitations on Internet connectivity, which are currently restricted to computers and smartphones in Web 2.0, will eventually dissipate as a result of IoT (Internet of Things). This technology will facilitate the development of an array of new intelligent utilities.
Layers of Web 3.0
Web 2.0 was primarily propelled by the emergence of mobile technologies, social media, and cloud computing, whereas Web 3.0 is being supported by three layers of innovative technology advancements.
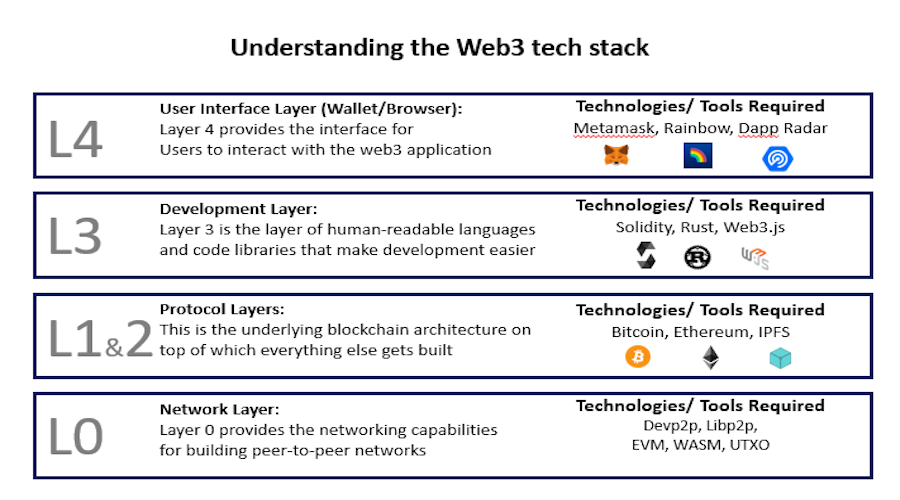
- Edge computing
- Decentralization
- Artificial intelligence & machine learning
- Blockchain
How does Web 3.0 work?
The underlying concept of Web 3.0 involves enhancing the speed, convenience, and overall efficiency of internet searches, including the ability to process complex search queries quickly and effectively within a shortened time frame.
In a web 2.0 application, users are required to interact with its user interface, and this interface communicates with its back-end, which in turn interacts with the application’s database. All of the code is stored on centralized servers and is delivered to users through an internet browser.
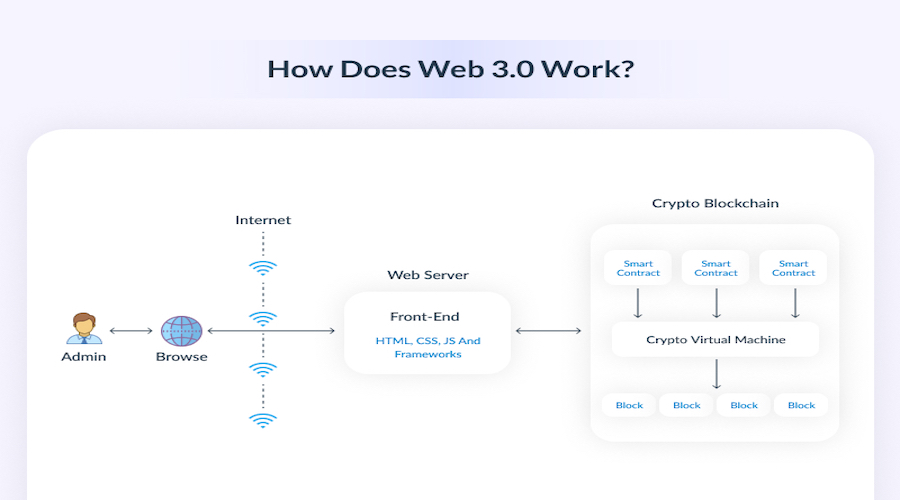
Web 3.0 is characterized by the absence of centralized storage for the application state and centralized web servers for storing the backend logic. Instead, a blockchain serves as the foundation for building decentralized applications, which operate on a non-centralized state machine maintained by anonymous nodes over the web.
The logic of your applications is determined by Smart Contracts, which are written by developers and implemented on a decentralized state machine.
Any individual who is willing to create a blockchain application can deploy their code onto this shared state machine. Despite this, the user interface remains remarkably similar to that of web 2.0.
Here’s a screenshot of a 3.0 web application in action:
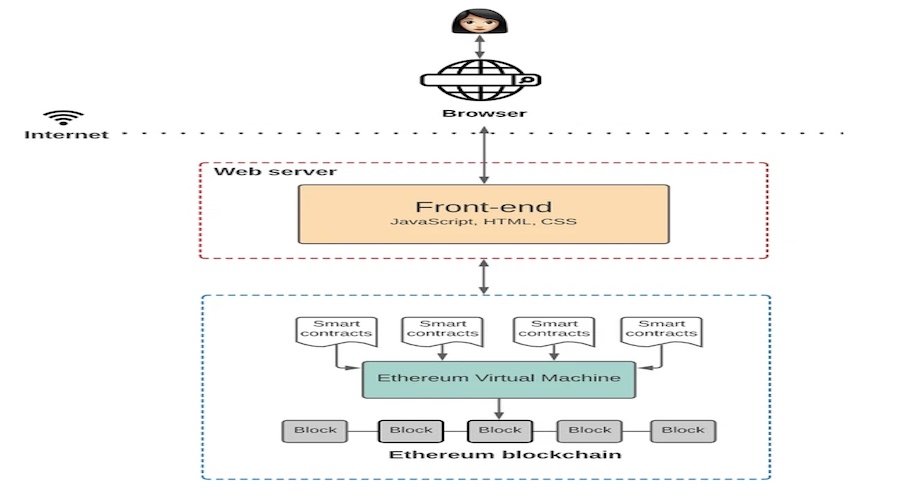
Architecture of Web 3.0
There are mainly 4 elements in the architecture that make up web 3.0:
- Ethereum Blockchain – This statement describes the Ethereum Blockchain, which consists of a network of equal nodes maintaining globally accessible state machines. People across the world can access the state machines and record information on them. The Ethereum Blockchain belongs to everyone on the network and is not owned by any entity specifically. Although users can input data into the Blockchain, they cannot update any existing data.
- Smart Contracts – The aforementioned programs are those which operate on the Ethereum Blockchain and are formulated by application developers using high-level programming languages such as Solidity and Vyper. Their purpose is to determine the rationale behind state changes.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) – The purpose of these machines is to execute the predetermined logic within Smart Contracts, and they process changes in state that occur within the state machine.
- Front End – Similar to any other application, the user interface defines the user interface logic. However, it also connects with Smart Contracts that determine the application logic. This demonstrates how the user interface operates in conjunction with the underlying Smart Contracts, allowing for seamless interaction and integration between both components.
Advantages of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is expected to revolutionize the way we experience the internet, as it will make it smarter, more secure, and transparent. As a result, browsing the web will become more efficient, and the interactions between humans and machines will be more effective. Here are some of the top benefits of Web 3.0 technology:
Privacy and data control
The foremost benefit of encrypting data is that end users will be able to secure their information from being disclosed to any party. Under no circumstances will the encryption be broken, preventing large organizations such as Google or Apple from controlling or utilizing individuals’ personal information for their own benefit. Thus, the end users will have complete ownership and privacy of their information.
Seamless service
The implementation of a decentralized data storage system ensures that users can access data in any circumstance. Through the provision of multiple backup copies, users benefit even in the event of server malfunction.
Moreover, it is impractical for any government entity or organization to be able to halt any website or service. As a consequence, the likelihood of account suspension and denial of distributed services will be significantly reduced.
Transparency
Regardless of the blockchain platform utilized by end-users, they are obliged to monitor their data and validate the code underlying the platform. Most non-profit organizations pioneer in the development of blockchain platforms, thus providing open-source blockchain platforms that facilitate transparent design and development procedures. This serves to eliminate the user’s dependence on the development organization.
Open data accessibility
The data will be accessible from anywhere and any device. We aim to enhance the data collection and accessibility for users from all around the world by enabling smartphones and other connected devices to access data on computers through synchronization.
The evolution of Web 3.0 will lead to an expansion of interaction on a larger scale, encompassing seamless payment systems, richer information streams, and reliable data transmission. This will be made possible by the ability to interact with any machine directly without the need for intermediaries to collect fees, thus providing a higher level of accessibility and reducing transaction costs.
Unlimited platform
Due to the fact that everyone can access the blockchain network, users have the ability to create their own unique address or interact with the network. Additionally, users are not restricted on the network based on gender, income, geographical location, or their social status. This feature empowers users to seamlessly transfer their assets or wealth anywhere in the world quickly.
Create unique profile
The advent of web 3.0 has eliminated the need for users to create separate personal profiles for different platforms. A single profile will suffice across all platforms, enabling users to retain complete ownership over their specific information.
In the absence of user consent, no company can access their data or verify its accuracy. However, users hold the right to opt for sharing their profiles and selling their data to advertisers or brands.
Advanced data processing
Web 3.0 offers benefits for problem-solving tasks and in-depth knowledge creation. This technological advancement utilizes artificial intelligence to extract valuable information from a vast amount of data. Furthermore, users are expected to benefit from predictive customer demand and personalized customer service, which are crucial for the growth of developing businesses.
Disadvantages of Web 3.0
Furthermore, there exist several challenges pertaining to the implementation of web 3.0. The management of personal data and reputation will become more critical than ever before. Below are the foremost challenges associated with the deployment and utilization of web3:
Advanced device requirements
Machines that are less advanced will not be capable of providing the benefits of web 3.0. The features and characteristics of the devices will need to be expanded in order to make the technology accessible to a wider audience globally. As of now, the number of individuals who can access web 3.0 will be limited.
Web 1.0 sites will become obsolete
If web 3.0 becomes the standard on the internet, any website that relies on web 1.0 technology will become obsolete. The older technology lacks the ability to update its features to match the new technology. This means that those websites will become significantly outdated and thereby lose their competitive advantage over newer websites.
Not ready for mass adoption yet
The Web3 technology is becoming more intelligent, efficient, and accessible. Nonetheless, it is not fully ready for wide-scale adoption, requiring extensive research on technological advancements, security laws, and data utilization to accommodate user needs.
Demand for reputation management will increase
When user information is more readily available and less anonymous through web 3.0, the management of reputation becomes a more important concern. In other words, brands and companies will need to maintain their name, reputation, and image online.
In order to outpace competitors, companies will be required to assist their customers in obtaining important market information, valuable business acumen, engaging content, and advanced internet marketing. As a result, reputation management will become more imperative than ever.
Complex function
Web 3.0 is a complex technology that may cause hesitation for new users. It is a fusion of previous generation web tools and advanced technologies such as AI and blockchain, which enhances user connectivity and experience on the internet.
This implies that only the latest advanced devices can process web 3.0, creating difficulties for individuals or businesses that do not have the means to purchase such devices. As technologically proficient users stand to benefit the most from this technology, the complex nature of web 3.0 has the potential to impede its global adoption.
Web 3.0 Application
The incorporation of blockchain technology in Web 3.0 enables the expansion of application and service offerings, including but not limited to:
- NFT Non-fungible tokens (NFT): The aforementioned tokens are singular and stored within a blockchain that utilizes a cryptographic hash function for secure storage.
- DeFi. Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, is an innovative application of the Web 3.0 concept wherein decentralized blockchains are utilized as the foundation for financial services that break free from the constraints of the traditional centralized banking infrastructure.
- Cryptocurrency. Digital currencies, such as Bitcoin, are generated through Web 3.0 applications, which create a new currency system aimed at separating from the traditional cash world.
- dApp. Decentralized applications, also known as DApps, are software applications created on the blockchain platform, which utilize smart contracts to enable the provision of services through a programmed ledger. These applications are designed to provide a distributed and secure system, free from third-party control, allowing for increased transparency, immutability, and accessibility to users.
- Cross-chain. In the realm of Web 3.0, there exist numerous blockchains, and to establish channels of communication between them, Cross-chain connectors are deployed.
- DAOs. DAOs are established with the aim of becoming organizational entities for Web 3.0 services, offering various decentralized structures and management approaches.
What is Yield Farming? Gain a comprehensive understanding of the terminology associated with Yield Farming
The concept of Yield Farming, prominent Yield Farming platforms, and the associated risks and opportunities are explored in this article,...
Read moreWhat is Initial DEX Offering (IDO crypto)? Does playing IDO really give you a 100% chance of winning?
One may inquire as to why the Initial DEX Offering (IDO) has gained widespread popularity and whether investing in IDO...
Read moreWhat is ERC – 20? Advantages, disadvantages & how to create ERC- 20 network tokens
In this article, we will explore ERC-20 and ERC-20 tokens along with their applications and advantages and disadvantages. For those...
Read moreWhat is Airdrop Crypto? Instructions for making airdrop coins in the Crypto market
What is Airdrop and how many forms of Airdrop Crypto exist? Discover the limitations and effective instructions on how to...
Read moreWhat is DAO? Limitations and Investment Potential of DAO in Crypto
Understanding the terminologies used in the field of cryptocurrency is crucial for individuals involved in Crypto market participation or intending...
Read moreWhat is zkEVM? Classification of groups zkEVM
ZkEVM is an abbreviation for the term "Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine". It is a protocol that enables the execution of...
Read moreWhat is web3 technology? How to invest in Web3 in 2023
The emergence of Web 3.0 following Web 2.0 has brought about increased flexibility and superior interaction capabilities compared to its...
Read moreWhat is move to earn? best move to earn crypto in 2023
In the current GameFi market, it is possible to combine the seemingly unrelated tasks of earning money and improving one's...
Read moreWhat does NFT crypto stand for: Clarifying the Significance of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) through technical examination
Non-fungible token (NFT) art are digital assets stored on a blockchain that depict physical or non-physical items, such as digital...
Read moreWhat are play to earn (P2E) Games? How to earn money with play game crypto?
Play to Earn has emerged as a popular trend in mid-2021, leading to a notable increase in the activity of...
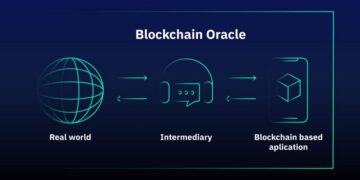
Read moreWhat is an oracle in blockchain? Top blockchain oracle projects 2023
The intended function of blockchain technology was never to operate in isolation from the larger economic ecosystem. Despite the challenges...
Read moreBinance account sign up: What is binance account? how to create binance account?
Numerous cryptocurrencies are supported by Binance and its proficiency in ensuring swift exchange operations between volatile coins and fiat currencies...
Read moreWhat is a defining feature of the Metaverse Crypto? What does the term Metaverse refer to?
We have heard numerous prominent figures, such as Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook, and Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, expound...
Read moreWhat are AI Tokens? Best AI Coins & Tokens to Invest in
The predicted impact of artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to revolutionize various sectors, including the field of cryptocurrency. The AI...
Read moreWhat are Fan Tokens? How Binance Fan Tokens are Revolutionizing the World of Sports and Entertainment?
The Fan Token is a term that has been shared by the CEO of the cryptocurrency exchange CZ on Twitter,...
Read more