The journey towards the creation of the atomic bomb was initiated by a moment of profound realization in London. Subsequently, the Manhattan Project culminated in an event of great consequence, namely, the detonation of the first nuclear bomb on the 16th of July, 1945.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhere did the idea of building an atomic bomb come from?
While waiting to cross the road in the vicinity of Russell Square in London, Leo Szilard conceived an idea on 12 September 1933, which ultimately led to the catastrophic event of dropping an atom bomb on Hiroshima by the United States approximately 12 years later, resulting in the tragic death of an estimated 135,000 people.
Who created the first atomic bomb?
Prior to the initiation of the Manhattan Project in autumn of 1942, Oppenheimer’s reputation as an extraordinary theoretical physicist had already taken root. Furthermore, he had delved deep into the realm of atomic weaponry and spent the preceding year conducting research on rapid neutrons. This entailed calculating the necessary amount of material for an atomic bomb and analyzing its potential efficiency.

Despite Oppenheimer’s lack of substantial managerial expertise and past dealings with Communist movements, General Leslie Groves identified his exceptional scientific aptitude. Subsequently, within three years of Groves choosing Oppenheimer to spearhead weapons production. The United States launched two atomic bombs on Japan. Oppenheimer’s tenure as director at the Los Alamos Laboratory was evident in his remarkable success, making him a suitable candidate for the position.
Biography j. Robert Oppenheimer
Early Life
Born on April 22, 1904 into a family that was involved in the Ethical Culture Society. an offshoot of American Reform Judaism that was established and led by Dr. Felix Adler. Oppenheimer was exposed to a progressive society that laid emphasis on aspects such as civic responsibility, social justice, and secular humanism. Oppenheimer’s enrollment in the Ethical Culture School, which was founded by Dr. Felix Adler, occurred in September 1911. And his exceptional academic abilities were evident early on. At the age of ten, he was already studying subjects such as chemistry, minerals, and physics. With his knowledge and skill so advanced that the New York Mineralogical Club invited him to deliver a lecture, unaware that he was merely a twelve-year-old boy.

The individual in question attained the honor of valedictorian in 1921 upon completing high school. However, he was stricken with a severe case of dysentery which jeopardized his health to the brink of death, hence causing a delay in his enrolment at Harvard. Due to his prolonged convalescence, his parents orchestrated his stay in New Mexico during the summer of 1922 to seek rejuvenation and recover from the ailment as the state was recognized to be a retreat for individuals seeking restoration of health.
Accompanied by high school teacher Herbert Smith as his mentor and guide, Robert resided at a dude ranch located 25 miles northeast of Santa Fe. Utilizing this location as a base, he embarked on numerous five- or six-day horseback excursions through the expanse of the wilderness. This endeavor proved quite fortifying to Oppenheimer’s overall well-being and engendered within him a profound affinity for the desert high country.
In September of 1922, Oppenheimer was admitted to Harvard where he completed his studies in three years, showcasing exceptional proficiency across multiple disciplines. Although his field of specialization was chemistry, Oppenheimer eventually discovered that his fervor for physics had taken precedence.
Oppenheimer embarked on his postgraduate studies in physics at Cavendish Laboratory located in Cambridge, England in the year 1925. The exceptional J. J. Thomson, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1906 for the discovery of the electron, generously offered to mentor Oppenheimer during his tenure as a student. While at Cavendish, Oppenheimer discovered his aptitude for theoretical rather than experimental physics, leading him to accept an invitation extended by Max Born, the director of the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Göttingen, to further his studies in Germany.
Robert Oppenheimer was fortunate to have been present in Europe during a crucial epoch in the field of physics. During this period, European physicists were pioneering the groundbreaking theory of quantum mechanics. Following his graduation with a doctorate in 1927, Oppenheimer assumed professorships at both the California Institute of Technology and the University of California, Berkeley. During his time at Berkeley, he developed a close friendship with the brilliant experimental physicist, Ernest Lawrence, who is renowned for his invention of the cyclotron. In honor of their friendship, Lawrence even named his second son after Oppenheimer.
Later Years
Following the culmination of the war, Oppenheimer assumed the role of an advisor for the Atomic Energy Commission and endeavored to advocate for global arms control. From 1947 onwards, he served as the director of the Institute for Advanced Study positioned in Princeton, New Jersey, where he summoned numerous prominent scientists, fueled by a shared pursuit for knowledge acquisition. One of his notable quotes during this period was, “What we cannot comprehend, we elucidate to each other.”
During the Second Red Scare, Oppenheimer’s security clearance was canceled when his prior Communist leanings were brought up in a hearing. His clearance was set to expire in 32 hours, but it was revoked due to his opposition to the development of the hydrogen bomb, which made him some political enemies. The revocation of his clearance deprived him of his political influence, while scientists were left infuriated by Oppenheimer’s ill-treatment and expressed their strong condemnation of Edward Teller, who gave evidence against him during the trial.
In 1960, the World Academy of Art and Science was established by a group of distinguished intellectuals, which included Albert Einstein, Bertrand Russell, Joseph Rotblat, and the subject of this discussion. His global outreach as a lecturer persisted following this event, and he was recognized with the Enrico Fermi Award in 1963. Tragically, he passed away from throat cancer in 1967.
J. Robert Oppenheimer’s Timeline
- 1904 Apr 22nd Born in New York, New York.
- 1911 Sep Enrolled in the Ethical Cultural School in New York City.
- 1921 Graduated as valedictorian of his high school class.
- 1922 After being bedridden with dysentery, spent the summer in New Mexico to recuperate.
- 1922 Enrolled at Harvard University.
- 1925 Began graduate work in physics at Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge, England under J. J. Thomson.
- 1926 Moved from Cavendish Laboratory to the University of Göttingen to finish his graduate studies under Max Born.
- 1927 Received Ph.D. in Physics from the University of Göttingen.
- 1927 Joined the faculty at the University of California, Berkeley, and Caltech.
- 1942 Jan Organized a program on fast neutron theoretical physics at the University of California at Berkeley.
- 1942 Jun Joined the Chicago Met Lab to lead an effort on fast neutron physics, and prepared an outline for the entire neutron physics program.
- 1942 Jul to 1942 Sep Assembled theoretical study group in Berkeley to examine the principles of bomb design. Emerged as the natural leader.
- 1942 Sep 29th Proposed that a “fast-neutron lab” to study fast neutron physics and develop designs for an atomic bomb be created.
1942 Oct 15th General Leslie R. Groves asked J. Robert Oppenheimer to head Project Y, planned to be the new central laboratory for weapon physics research and design.
- 1942 Oct 19th Vannevar Bush approves Oppenheimer’s appointment in meeting with Oppenheimer and General Groves.
- 1942 Nov 16th General Groves and Oppenheimer visit the Los Alamos, NM mesa in New Mexico and select it for “Site Y.
- 1943 to 1945 Director of the Los Alamos Laboratory.
- 1945 Jul 16th To his immense relief, witnessed the successful Trinity test.
- 1945 Oct 16th Resigns as director of Los Alamos Laboratory, accepting a post at CalTech.
- 1947 Became director of the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey.
- 1954 Jun 29th Oppenheimer’s security clearance was revoked by the US Atomic Energy Commission, just 32 hours before it was set to expire.
- 1963 Dec 2nd Received the Enrico Fermi Award.
- 1967 Feb 18th Died in Princeton, New Jersey.
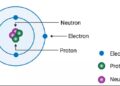
Who discovered electrons protons and neutrons?
The discovery of neutrons, which possess no electric charge and nearly the same mass as protons while remaining electrically neutral,...
Read moreWho is the painter of The Mona Lisa?
The Louvre Museum houses one of the most iconic portraits in the history of art, namely the Mona Lisa painting....
Read moreWho makes Genesis vehicles?
The Hyundai Motor Group produces luxurious automobiles under the name of Genesis. In 2015, the company announced its intention to...
Read moreWho discovered United States of America?
The response to the aforementioned inquiry appears to be apparent for the majority of individuals, as they were educated in...
Read moreWho created the first atomic bomb formula?
The journey towards the creation of the atomic bomb was initiated by a moment of profound realization in London. Subsequently,...
Read moreWho has the most followers on instagram in the world?
In response to an inquiry of utmost interest, it has been revealed that the individual with the most followers on...
Read moreQuotes about friends who are fake
The end of a friendship can be an excruciatingly painful experience, potentially overshadowing other kinds of heartbreak. The betrayal of...
Read moreWho is the top 10 richest people in Asia?
The ever-changing wealth landscape in Asia has continually garnered international attention, as a vast number of individuals have left their...
Read moreWho is the most richest person in the world currently?
With a net worth of $239.3B, Elon Musk currently holds the top position on the list of the world's wealthiest...
Read moreHow deep is the wreck of The Titanic?
On April 15, 1912, the RMS Titanic endured a tragic fate in the North Atlantic Ocean as it collided with...
Read moreThe biggest country in the world by population
Data published by the World Bank reveals that in 2021, the 25 most populous countries in the world accounted for...
Read more