The concept of Yield Farming, prominent Yield Farming platforms, and the associated risks and opportunities are explored in this article, as Yield Farming gains increasing attention within the crypto and DeFi communities. However, to effectively and securely generate profit through this method, it is crucial to thoroughly understand its operational mechanics. Thus, we invite readers to follow along as we delve into this subject matter.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Yield Farming?
The term Yield Farming refers to the practice wherein users endeavor to generate maximum profit from their crypto assets by providing liquidity to DeFi (Decentralized Finance) protocols.

The term “Yield” translates to profit, and “Farming” translates to cultivation. “Yield Farming” can be defined as profit cultivation. For the purpose of this discourse, the technical terminology of “Yield Farming,” “Yield,” “Farming,” and “Farm” will be preserved.
How Yield Farming Works
Yield Farming is closely associated with the Automated Market Maker (AMM) model. Popular AMM models include platforms like Uniswap, Mooniswap, and Balancer.
In Yield Farming, Liquidity Providers (LPs) contribute liquidity to the liquidity pools of the protocol. These pools are essentially smart contracts that contain funds. The pools enable users to borrow, lend, or trade various tokens.
The revenue generated by the Liquidity Pool consists of transaction fees incurred by end-users when carrying out activities such as borrowing, lending, and exchanging tokens within the pool. Said revenue is then distributed amongst the LP based on the percentage of liquidity they have provided in the pool.
In addition to revenue generated from fees, certain protocols also implement bootstrapping liquidity for the protocol by distributing native tokens to LPs who have provided liquidity to their protocol (potentially across the entire protocol pool or specific designated pools). This process is commonly referred to as Liquidity Mining.
The concept of Liquidity Mining can be understood as a narrower term than Yield Farming, specifically in the sense that Liquidity Providers (LPs), in addition to earning money by supplying liquidity, also receive a certain amount of new tokens.
Prominent Yield Farming platforms are readily apparent within the industry
Some popular Yield farming platforms in DeFi:
- MakerDAO: Use Maker mint for DAI, use DAI for yield farming in other protocols like Compound.
- Compound: Provide liquidity into Compound to farm COMP and earn profits from borrowing and lending activities.
- Uniswap: Provide liquidity into the pool to collect transaction fees.
- Balancer: Farm BAL and other governance tokens support the pool on Balancer.
- Synthetix: Use SNX mint sUSD, bring sUSD to provide liquidity in pools on other platforms.
- Aavee: Borrow and lend money, flash loans. From there, providing liquidity on other platforms, farming more.
- Curve Finance: Provide liquidity and earn fees, interest and CRV.
- yEarn Finance: Provide liquidity and collect fees, farm YFI.
Effects of Yield Farming
It is undeniable that Yield Farming has had a significant impact on the development of DeFi. Ever since the launch of Liquidity Mining with the governance token COMP by Compound, DeFi has seen an incredible surge in growth. This event sparked the emergence of similar programs by other projects, all aimed at attracting liquidity into the protocols. As a result, the DeFi space has never been hotter.
The transfer of liquidity from one protocol to another, combined with the significant increase in value of the governance token, has caused unproductive capital. As a solution, a shift towards Defi protocols for farming and profit generation has been initiated, ultimately transforming unproductive capital into productive capital.
As funds flow into the decentralized finance (DeFi) space, numerous DeFi projects are emerging with innovative distribution mechanisms that leverage existing protocols. An example of such a project is Yam Finance.
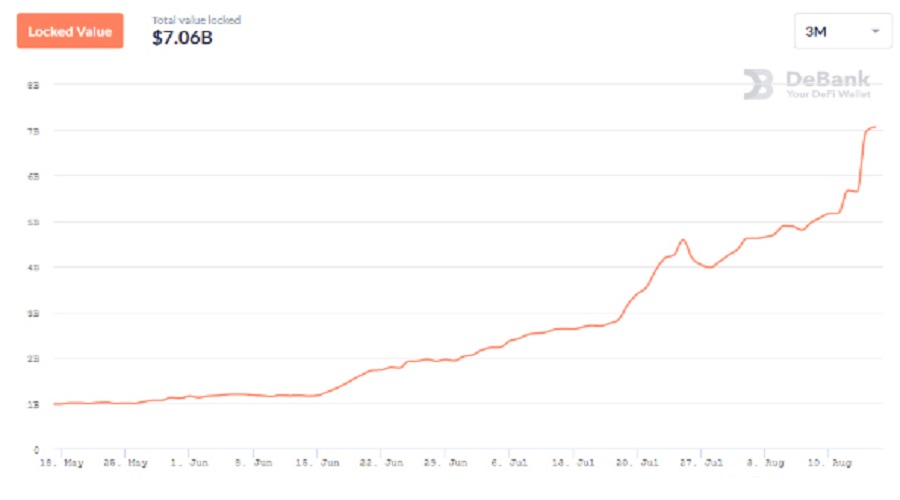
The outcome reveals that the aggregate amount of assets locked within the DeFi ecosystem, also known as Total Value Locked (TVL), has surged over sevenfold, escalating from one billion to seven billion US dollars within a mere three-month timespan.
For those who are not familiar with Total Value Locked (TVL), it is a metric used to gauge the “health” of yield farming and DeFi platforms. TVL measures the amount of crypto assets locked within DeFi protocols, such as lending protocols and other forms.
Furthermore, both governance tokens and DeFi-related projects have experienced significant growth in recent times.

Upon examining the chart above, it is evident that the price of COMP reached its all-time high (ATH) in June, owing to the significant increase in demand for COMP resulting from COMP farming.
Risks of Yield Farming
Most Yield Farming strategies offer APR/APY (Annual Percentage Rate/Annual Percentage Yield) that are largely complicated and require users to have a deep understanding of what they are doing. If individuals do not fully comprehend how the transactions are operating, there is a high likelihood of financial loss.
Some risks of Yield Farming:
- Smart Contract Risks: Most protocols are developed by small teams with limited resources, which increases the likelihood of bugs in smart contracts due to the lack of budget for audits. Even audited protocols can still have vulnerabilities and be subject to theft, as evidenced by the cases of Bzrx and Curve.
- System Design Risks: In certain protocols such as Uniswap, liquidity provision may result in LPs incurring rare impermanent losses when the price of an asset in the pool experiences significant fluctuations. Alternatively, LPs may face a complete withdrawal of funds when providing liquidity, as was witnessed in the case of Balancer.
- Risk of Liquidation: The collateral assets may experience significant fluctuations and the position of the user may be liquidated during market volatility.
- The emergence of a bubble risk in the DeFi market occurred following the launch of Liquidity mining by COMP, leading to widespread FOMO within the DeFi community.
Yield Farming – Whales Game
The winners of this game are the Whales – individuals who hold tens of millions of dollars and engage in farming, thus earning governance tokens. Whales merely have a vested interest in the project, investing large sums of money to decrease the distribution ratio of small players. Retail investors who experience FOMO early on can earn substantial profits or lose their invested amounts altogether. It is worth noting that those who suffer losses are often those who joined the game later on, when the price had already risen beyond reason.
In order to mitigate risks, it is advisable for individuals to engage in early farming and purchase a reasonable amount of governance tokens at an acceptable price, which could be likened to playing the lottery.
Some thoughts on Yield Farming
On the first point, Yield Farming has ushered in a new era for DeFi by utilizing the bootstrapping protocol technique through liquidity mining, which could be considered a method to effectively entice users in the short term.
The second point to consider is that with the launch of Yield Farming protocol, it may impact other protocols positively to rise together. However, this inter-dependency among them may not sustain if the yield decreases gradually, as evidenced by the notable examples of yEarn, bootstrapping for both yEarn, and Curve, as well as Balancer.
Both ideas 1 and 2 are only short-term.
According to Theo Jesse Walden (former colleague of a16z), the long-term success of DeFi protocols will depend on both users and creators. While incentivizing profit through hacking can drive short-term user growth, the true game-changer lies in building and owning a product or service that billions of people will use daily, resulting in long-term wealth creation. This highlights the need for a strategic focus on user experience, product design, and innovation in the ongoing development of DeFi protocols.
Summary
This article provides a comprehensive overview of one of the hottest buzzwords in the current landscape of decentralized finance – “Yield Farming”. Despite the highly enticing short-term profits that Yield Farming yields, it is crucial for the innovators in the DeFi space to ensure that their products offer practical benefits that are intimately tied to our daily lives, so as to prevent it from being merely a fleeting trend.
It is hoped that Yield Farming will be observable not only within the crypto space but also within the conventional financial mainstream in the future.
The above information was researched by the team at 247btc.net. We hope that this information will be helpful to our readers. However, please note that this is not investment advice, but rather an informational channel. Therefore, investment decisions should be carefully considered.
What is Yield Farming? Gain a comprehensive understanding of the terminology associated with Yield Farming
The concept of Yield Farming, prominent Yield Farming platforms, and the associated risks and opportunities are explored in this article,...
Read moreWhat is Initial DEX Offering (IDO crypto)? Does playing IDO really give you a 100% chance of winning?
One may inquire as to why the Initial DEX Offering (IDO) has gained widespread popularity and whether investing in IDO...
Read moreWhat is ERC – 20? Advantages, disadvantages & how to create ERC- 20 network tokens
In this article, we will explore ERC-20 and ERC-20 tokens along with their applications and advantages and disadvantages. For those...
Read moreWhat is Airdrop Crypto? Instructions for making airdrop coins in the Crypto market
What is Airdrop and how many forms of Airdrop Crypto exist? Discover the limitations and effective instructions on how to...
Read moreWhat is DAO? Limitations and Investment Potential of DAO in Crypto
Understanding the terminologies used in the field of cryptocurrency is crucial for individuals involved in Crypto market participation or intending...
Read moreWhat is zkEVM? Classification of groups zkEVM
ZkEVM is an abbreviation for the term "Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine". It is a protocol that enables the execution of...
Read moreWhat is web3 technology? How to invest in Web3 in 2023
The emergence of Web 3.0 following Web 2.0 has brought about increased flexibility and superior interaction capabilities compared to its...
Read moreWhat is move to earn? best move to earn crypto in 2023
In the current GameFi market, it is possible to combine the seemingly unrelated tasks of earning money and improving one's...
Read moreWhat does NFT crypto stand for: Clarifying the Significance of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) through technical examination
Non-fungible token (NFT) art are digital assets stored on a blockchain that depict physical or non-physical items, such as digital...
Read moreWhat are play to earn (P2E) Games? How to earn money with play game crypto?
Play to Earn has emerged as a popular trend in mid-2021, leading to a notable increase in the activity of...
Read moreWhat is an oracle in blockchain? Top blockchain oracle projects 2023
The intended function of blockchain technology was never to operate in isolation from the larger economic ecosystem. Despite the challenges...
Read moreBinance account sign up: What is binance account? how to create binance account?
Numerous cryptocurrencies are supported by Binance and its proficiency in ensuring swift exchange operations between volatile coins and fiat currencies...
Read moreWhat is a defining feature of the Metaverse Crypto? What does the term Metaverse refer to?
We have heard numerous prominent figures, such as Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Facebook, and Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, expound...
Read moreWhat are AI Tokens? Best AI Coins & Tokens to Invest in
The predicted impact of artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to revolutionize various sectors, including the field of cryptocurrency. The AI...
Read moreWhat are Fan Tokens? How Binance Fan Tokens are Revolutionizing the World of Sports and Entertainment?
The Fan Token is a term that has been shared by the CEO of the cryptocurrency exchange CZ on Twitter,...
Read more